他汀类药物
外观
(重定向自HMG-CoA还原酶抑制剂)
此条目需要扩充。 (2007年9月26日) |
| 他汀类药物 | |
|---|---|
| 药物种类 | |
 | |
| 用途 | 高胆固醇 |
| 生物靶标 | 羟甲基戊二酸单酰辅酶A还原酶 |
| ATC代码 | C10AA |
| 外部链接 | |
| MeSH | D019161 |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | 药物分类 |
他汀[1][2](英语:statin)或译斯他汀[3][4],又称他汀类药物(statin drugs[5])是一类抗高血脂药,学名羟甲基戊二酸单酰辅酶A还原酶抑制剂(HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor)或HMG-CoA还原酶抑制剂。他汀通过抑制胆固醇合成中的关键酶从而降低血液中胆固醇水平,可抑制胆固醇和甘油三酯的合成和分泌,为临床上应用最广泛的一类调脂药物。
Colin Baigent教授和他的同事们针对老龄人高血脂引起的心血管疾病预防做了研究,调查接近十九万的样本,实验的结果显示因他汀类有降低心血管疾病的作用[6]。
药物
[编辑]- 阿托伐他汀 (英语:Atorvastatin)
- 西立伐他汀因不良反应已停售
- 氟伐他汀
- 洛伐他汀
- 美伐他汀
- 匹伐他汀 (英语:Pitavastatin)
- 普伐他汀
- 瑞舒伐他汀 (英语:Rosuvastatin)
- 辛伐他汀 (英语:Simvastatin)
作用
[编辑]- 血浆中的胆固醇来源有外源性和内源性两种途径。外源性胆固醇主要来自食物,可通过调节食物结构来控制摄入量;内源性的则在肝脏中合成。在肝细胞的细胞质中,由乙酸经26步生物合成步骤合成内源性胆固醇。
- 其中羟甲戊二酰辅酶A还原酶(3-羟基-3-甲基戊二酰辅酶A(HMG-CoA)还原酶)是该合成过程中的限速酶,能催化HMG-CoA还原为甲羟戊酸。此步骤是内源性胆固醇合成中关键一步,若抑制HMG-CoA还原酶,则内源性胆固醇合成减少。


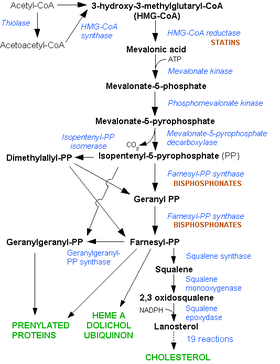
相互作用
[编辑]- 胆固醇可反馈抑制肝胆固醇的合成。它主要抑制HMG-CoA还原酶的合成。
- 胰岛素及甲状腺素能诱导肝HMG-CoA还原酶的合成,从而增加胆固醇的合成。
药理学
[编辑]点击基因、蛋白质和代谢产物的链接访问对应的介绍条目。 [§ 1]
他汀类药物途径 编辑
- ^ 这个相互作用途径可以在WikiPathways上编辑: Statin_Pathway_WP430.
安全性
[编辑]历史
[编辑]
- 1971年,日本科学家远藤章在研制抗胆固醇药物时,发现HMG-CoA还原酶与胆固醇之间的关系,因此推断微生物可制成胆固醇抑制剂。1973年,远藤团队从桔青霉菌(Penicillium citrinum)中分离出了一种抑制剂美伐他汀(mevastatin,Compactin,ML-236B)[8]。
- 1990年代末,由拜尔公司开发的西立伐他汀 (Cerivastatin),,与辉瑞公司极为成功的阿托伐他汀 (Lipitor) 进行竞争。上市仅8个月,销售额达$7亿美元,全世界约有600万人使用过西立伐他汀,有40例病人死亡与其严重的肌损伤不良反应有关,因此拜尔公司不得不于2001年8月在全球范围内停止销售西立伐他汀的所有制剂。
参见
[编辑]参考文献
[编辑]- ^ 张世阳,谈敏,胡世莲. 他汀相关性肌病[J]. 中国基层医药,2005,12:(11):1619-1620.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1008-6706.2005.11.104
- ^ 赵佳慧. 他汀与肾脏疾病[J]. 国际泌尿系统杂志,2008,28:(04):510-513.DOI:10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-4416.2008.04.022
- ^ 食品药物管理署. 降血脂藥吃對了嗎?. 卫生福利部.
- ^ 斯他汀類藥物. 乐词网. 国家教育研究院. (繁体中文)
- ^ 安瑗,王慧媛,赵志刚,等.他汀类药物的临床合理应用[J].实用药物与临床, 2011, 14(5):408-411.
- ^ More over-75s 'should take statins'. 2019-02-01 [2019-02-01]. (原始内容存档于2019-02-01) (英国英语).
- ^ Istvan ES, Deisenhofer J. Structural mechanism for statin inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Science. 2001, 292 (5519): 1160–4. PMID 11349148. doi:10.1126/science.1059344.
- ^ Liao and Laufs. Pleiotropic Effects of Statins.(2005) Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol:45:89-118.
外部链接
[编辑]- Statin pageArchive.is的存档,存档日期2012-12-23 at Bandolier, an evidence-based medicine journal (little content after 2004)

