长吻针鼹
外观
(重定向自西長吻針鼴)
| 长吻针鼹[1] | |
|---|---|

| |
| 科学分类 | |
| 界: | 动物界 Animalia |
| 门: | 脊索动物门 Chordata |
| 纲: | 哺乳纲 Mammalia |
| 目: | 单孔目 Monotremata |
| 科: | 针鼹科 Tachyglossidae |
| 属: | 原针鼹属 Zaglossus |
| 种: | 长吻针鼹[1] Z. bruijnii
|
| 二名法 | |
| Zaglossus bruijnii | |
| |
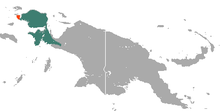
| 物种分布图 (绿色— 分布范围;橙色:可能已绝迹) | |
| 异名 | |
|
Zaglossus bruijni (Peters & Doria, 1876) [orth. error] | |
长吻针鼹(学名:Zaglossus bruijnii),又名原针鼹、三趾针鼹、五趾针鼹或曲喙针鼹,是地球上最原始的现生哺乳动物之一,近年来数量下降很快。
长吻针鼹仅分布于新几内亚岛,介乎海拔1300米至4000米,不过在南部低地及北部海岸却不见它们的踪影,也有可能存在于邻近的印尼萨拉瓦蒂岛。它们喜欢生活在高寒草原及潮湿山区森林。它不像澳大利亚针鼹吃蚂蚁及白蚁,而是吃蚯蚓。长吻针鼹比澳大利亚针鼹大,达到16.5千克重,吻长及可以向下,其刺混杂在长毛之间。前后肢均具3爪,爪坚硬锐利,适合挖掘。毛针鼹是异温动物;根据环境温度的不同,它们的温度可以在36到25C之间变化。同时,针鼹继续活跃,在最不利的条件下会冬眠。
长吻针鼹被世界自然保护联盟列为极危物种,数量因栖息地减少及狩猎而下降。[2]虽然狩猎长吻针鼹已被印尼及新几内亚政府所禁止,但传统的狩猎仍然继续。于2006年,保护国际在巴布亚省的福亚山脉发现大量的长吻针鼹。[3]
参考
[编辑]- ^ Template:MSW3 Monotremata
- ^ 2.0 2.1 Leary, T., Seri, L., Flannery, T., Wright, D., Hamilton, S., Helgen, K., Singadan, R., Menzies, J., Allison, A., James, R., Aplin, K., Salas, L. & Dickman, C. Zaglossus bruijnii. IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. 2016, 2016: e.T23179A21964204. doi:10.2305/IUCN.UK.2016-2.RLTS.T23179A21964204.en.
- ^ MSNBC staff and news service reports. 'Lost World' of wildlife found in Indonesia. MSNBC. 2006-02-10 [2008-01-22]. (原始内容存档于2012-10-25).
- Augee, M and Gooden, B. 1993. Echidnas of Australia and New Guinea. Australian National History Press ISBN 978-0-86840-046-4
- Flannery, T.F. and Groves, C.P. 1998 A revision of the genus Zaglossus (Monotremata, Tachyglossidae), with description of new species and subspecies. Mammalia, 62(3): 367-396
- Groves, C.P. Wilson, D.E. & Reeder, D.M. , 编. Mammal Species of the World: A Taxonomic and Geographic Reference (3rd ed.). Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press. 2005: 2. ISBN 978-0-8018-8221-0. LCCN 2005001870. OCLC 62265494. OL 3392515M. NLC 001238428.

